√70以上 shapes of s p d f orbitals ppt 254454-Shapes of s p d f orbitals ppt
S p d f Orbitals Isaiah Anderson Tomas Fernandez Ben Blasko What are Orbitals?Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are regions of space in which electrons can be found Each orbital can fit two electrons and different orbitals have different shapes The s sublevel has one spherically shaped orbital, while the p sublevel has three dumbbell shaped orbitalsFor example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2

Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families
Shapes of s p d f orbitals ppt
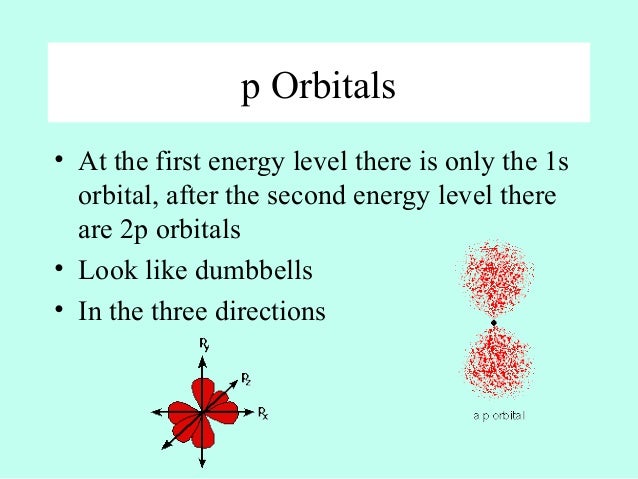
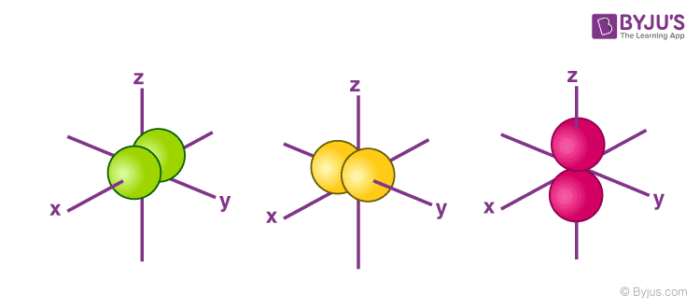
Shapes of s p d f orbitals ppt-P orbital • Unlike the spherically symmetric s orbitals, a p orbital is oriented along a specific axis All p orbitals have l = 1, and there are three possible values for m (1, 0, 1) Whenever m does not equal zero, the wave function is complex, which makes visualization of the wave function difficultThe shapes of p, d and forbitals are described verbally here and shown graphically in the Orbitals table below The three porbitals for n = 2 have the form of two ellipsoids with a point of tangency at the nucleus (the twolobed shape is sometimes referred to as a " dumbbell "—there are two lobes pointing in opposite directions from each other)
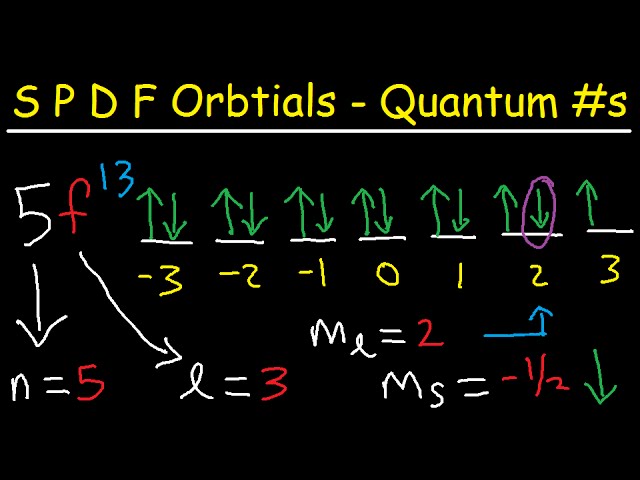


S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube
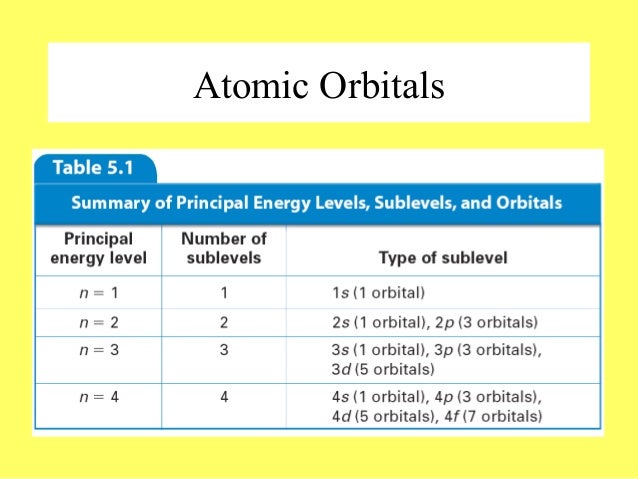
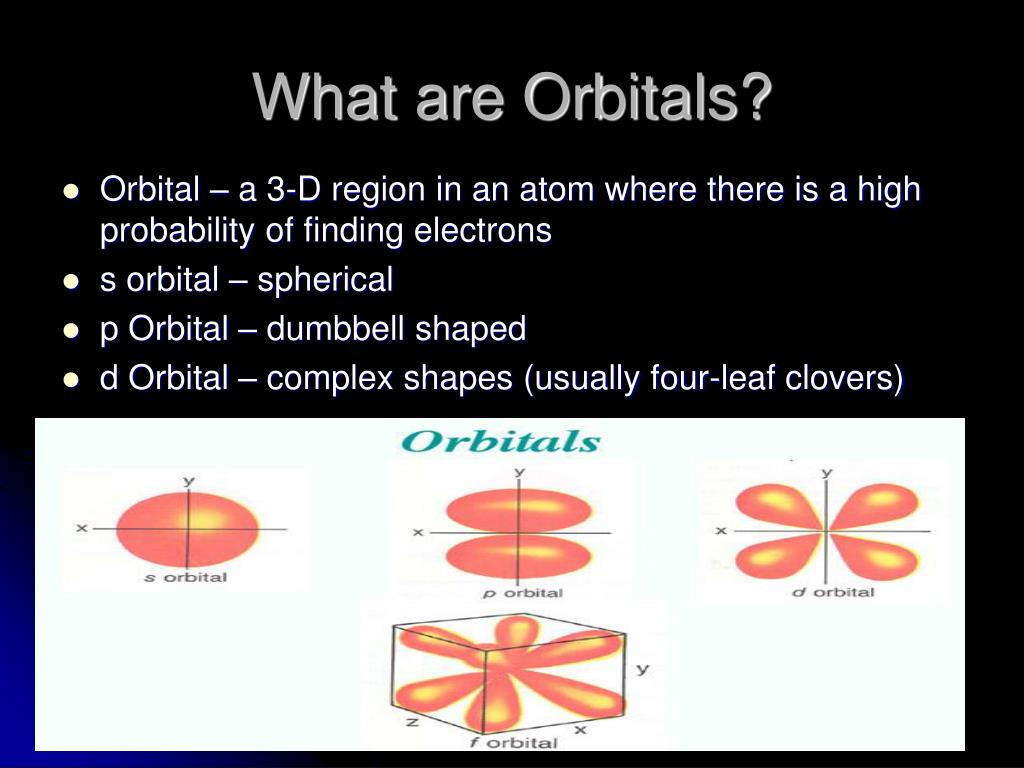
List the four orbital shapes The orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals Electrons fill orbitals with the lowest energy level possible firstAs shown in Table 1, the s subshell has one lobe, the p subshell has three lobes, the d subshell has five lobes, and the f subshell has seven lobes Each of these lobes is labeled differently and is named depending on which plane the lobe is resting in• Orbital – a 3D region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons • s orbital – spherical • p Orbital – dumbbell shaped • d Orbital – complex shapes (usually fourleaf clovers)
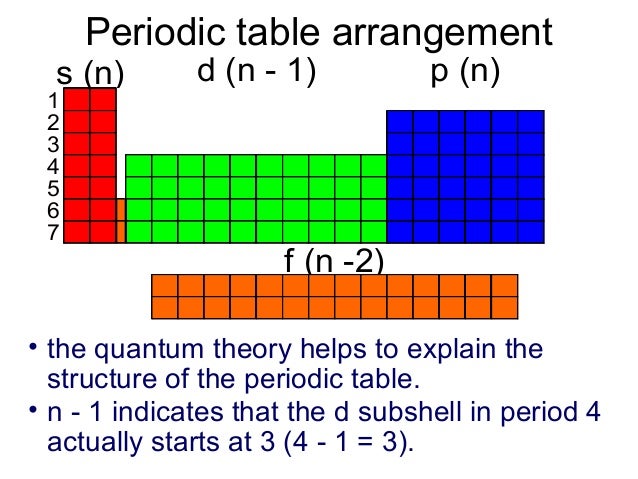
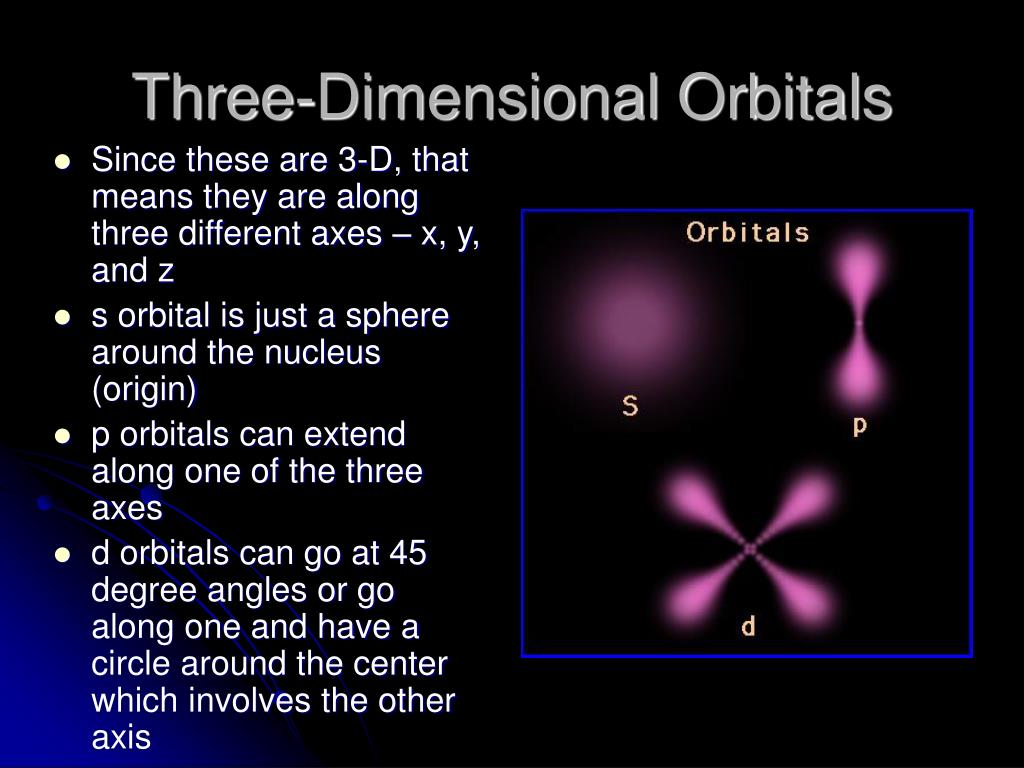
S Orbital Versus P Orbital While orbital numbers (eg, n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time The smallest sphere is 1sS P D F & the Periodic Table O The period # on the periodic table is equal to the number of energy levels (n) in an atom O Within each energy level there are sublevels O The periodic table is divided into blocks to represent each sublevel, with each orbital holding only 2 electrons s Block p Block d Block f Block 1sAre to arrange an orbital of that shape around the nucleus "s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!
How Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!The following figure shows the shapes of the s, p, and d orbitals 18 As shown in the top row of the figure (a), there are two s orbitals — one for energy level 1 (1s) and the other for energy level 2 (2s) The s orbitals are spherical with the nucleus at the center Notice that the 2s orbital is larger in diameter than the 1s orbitalSHAPES OF ATOMIC ORBITALS S, P, D and F


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels


Orbital Shape Orientationt
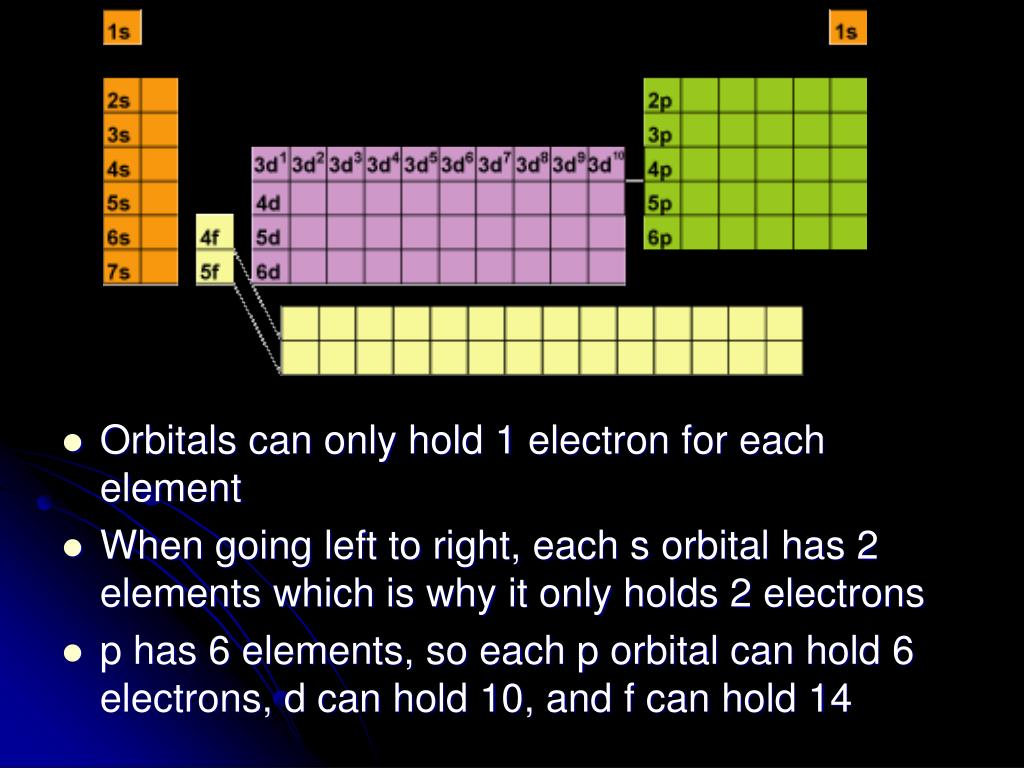
Playlist Link is given below for complete video lecture series 👇🏻https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PLEIbY8S8u_DIQX5hrfcPa4qMZk7XKStvhOrbital, Electron(1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellS p d f Orbitals Isaiah Anderson Tomas Fernandez Ben Blasko What are Orbitals?


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital
The letters s, p, d, and f were assigned for historical reasons that need not concern us All we have to do is remember the shapes that correspond to each letter Since an electron can theoretically occupy all space, it is impossible to draw an orbital All we can do is draw a shape that will include the electron most of the time, say 95% of the time We call this shape the 95% contour s ORBITALS4 Spin Quantum Number (ms) m s = ½ or ½ Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electron An electron can spin in only one of two directions (sometimes called up and down) The Pauli exclusion principle (Wolfgang Pauli, Nobel Prize 1945) states thatno two electrons in the same atom can have identical values for all four of their quantum numbersSummary p orbitals and d orbitals p orbitals look like a dumbell with 3 orientations p x , p y , p z ("p sub z") Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a clover shape The last d orbital resembles a p orbital with a donut wrapped around the middle 9
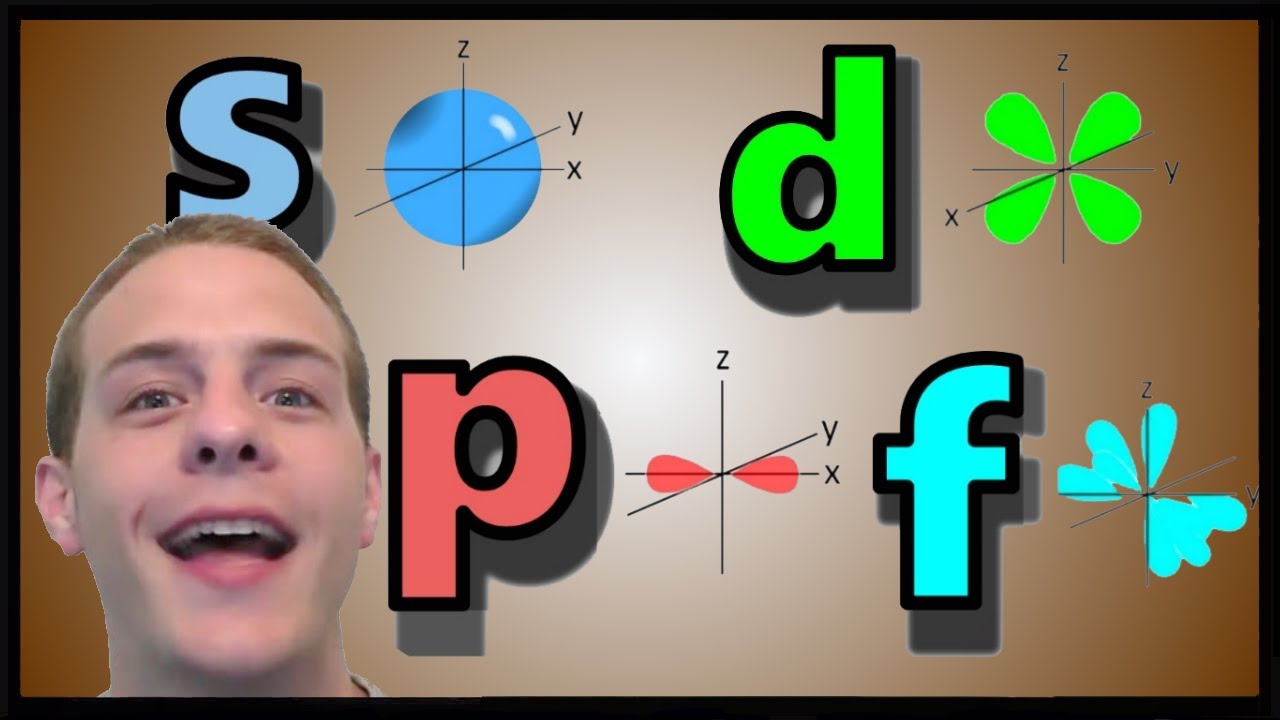


The Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Youtube


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic
There are two remaining p orbitals Next we show the phase pictures of combining the sp hybrid orbitals with fi rst one and then both of the remaining p orbitals Phase pictures loop Diagram Axes for you to draw the loop diagramS p d f Orbitals Isaiah Anderson Tomas Fernandez Ben Blasko What are Orbitals?Summary p orbitals and d orbitals p orbitals look like a dumbell with 3 orientations px, py, pz ("p sub z") Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a clover shape The last d orbital resembles a p orbital with a donut wrapped around the middle
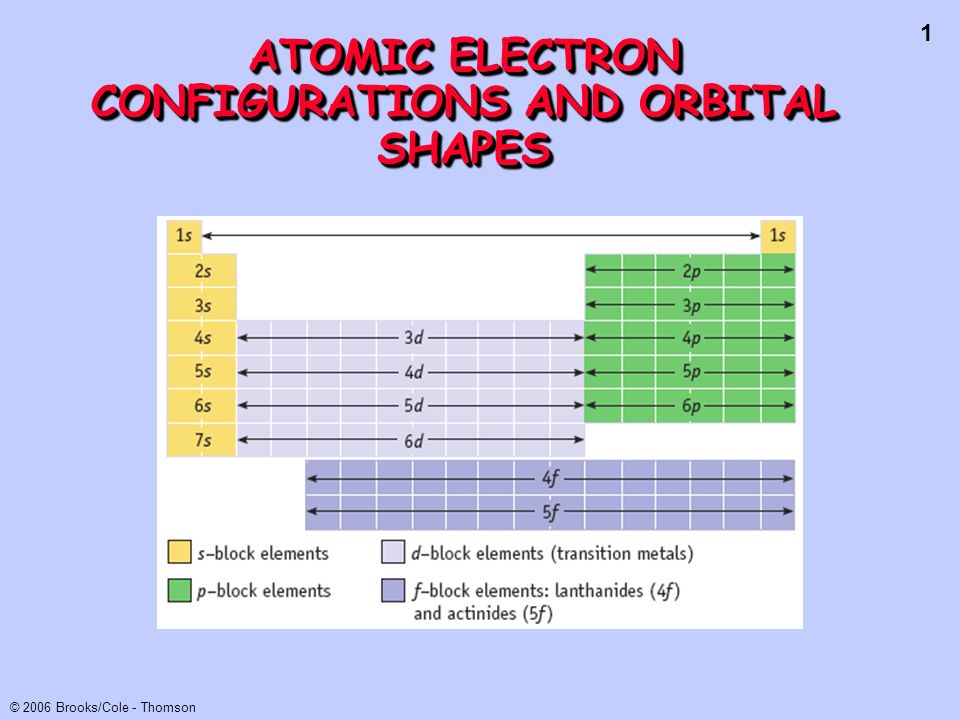


Atomic Electron Configurations And Orbital Shapes Ppt Video Online Download
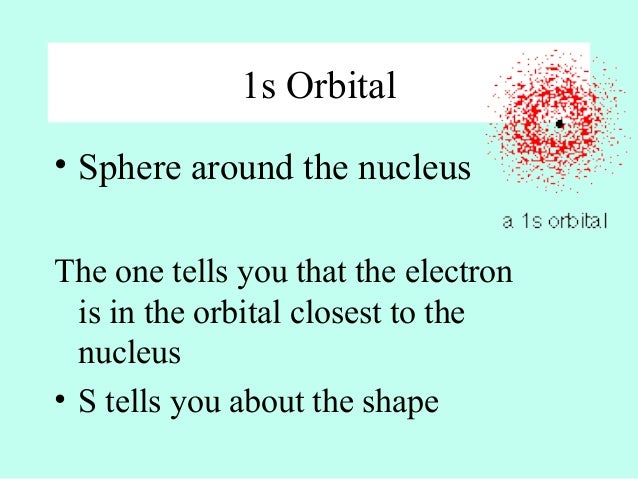


Orbital Shape Orientationt
In quantum chemistry Ψ 2 provides us with the electron density it defines the size and shapes of the familiar orbitals s, p, d, f, etc Figure 2 sin 2 x vs x The diagram above shows sin 2 x has identical nodes to sin x;An sp hybridized atom uses one s and one p orbital to make two sp hybrid orbitals;Describes the orientation of the orbital in space;
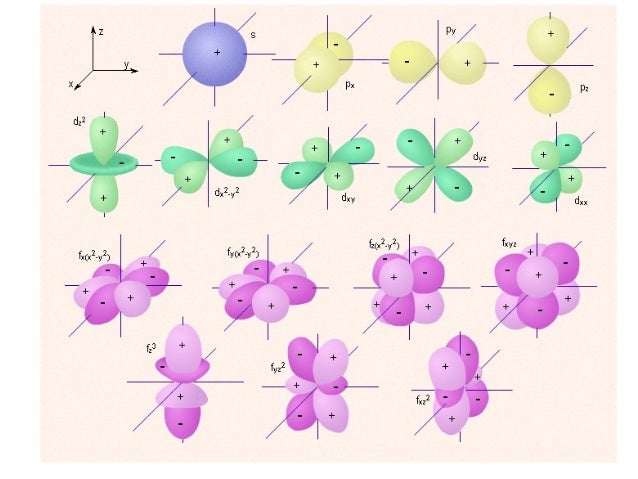


Orbital Shape Orientationt
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ShellAtomicModel-5a6ab592aded4bb7a1328f809e4f10da.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
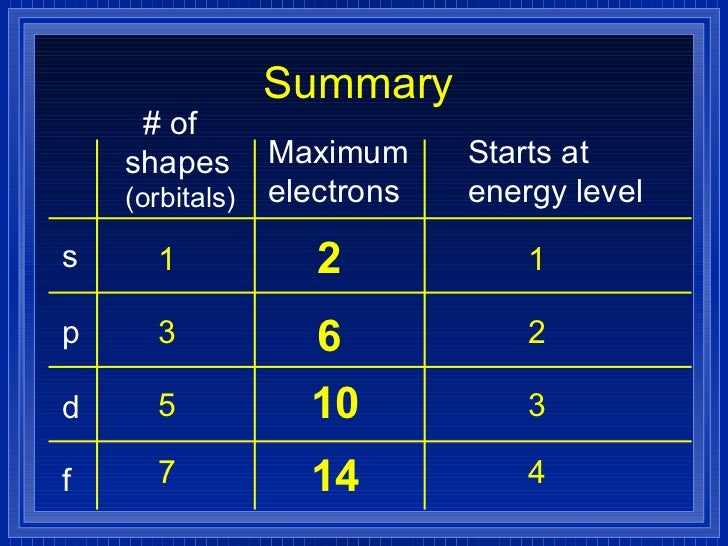
Maximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitalsAtomic orbitals are the three dimensional regions of space around the nucleus of an atom Atomic orbitals allow the atoms to make covalent bonds s, p, d and f orbitals are the most commonly filled orbitals As defined by the Pauli Exclusion Principle, only two electrons can be found in any orbital spaceShapes and Orientations of Orbitals We use your LinkedIn profile and activity data to personalize ads and to show you more relevant ads



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333



Geos 306 Fall 01 Lecture 2 The Nature Of The Atom
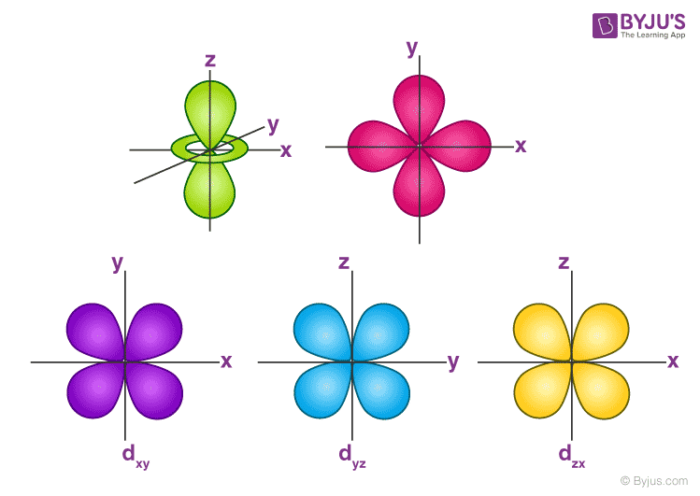
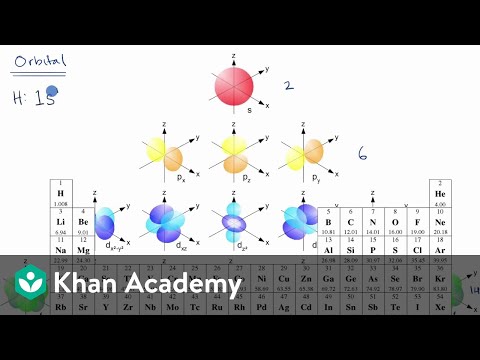
Therefore, we can say that there are about 3 p orbitals whose axes are mutually perpendicular Just like the s – orbitals, with an increase in size and energy of p orbitals quantum number ( 4p > 3p > 2p ), the size and energy of p orbitals also increase D – Orbitals Magnetic orbital quantum number for d orbitals is given as ( 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 )The shapes of the other orbitals are more complicated The letters s, p, d, f, originally were used to classify spectra descriptively into series called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental, before the relation between spectra and atomic electron configuration was knownP orbitals wavefunctions • There are three p orbitals for each value of n (p x, p y, p z) • The radial function is the same for all np orbitals • The angular terms are different different shapes (orientations) – Although 2p x, 3p x, 4p x have the same shape • Wave function for 2p and 3p orbitals R(r) Y(q f) sin( )sin() 4 3 ( ) 2 1 q



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333



Orbital Shape Orientationt
P Orbitals (l=1) Only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical As the value of l increases, the numbe\(r\) of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex Because the 2p subshell has l = 1, with three values of m l (−1, 0, and 1), there are three 2p orbitals Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) Electron Probability Distribution fo\(r\) a Hydrogen 2pP Orbitals (l=1) Only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical As the value of l increases, the numbe r of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex Because the 2 p subshell has l = 1, with three values of ml (−1, 0, and 1), there are three 2 p orbitalsInstead of being listed as a numerical value, typically 'l' is referred to by a letter ('s'=0, 'p'=1, 'd'=2, 'f'=3) Defines the shape of the orbital;



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333


Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation
• Orbital – a 3D region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons • s orbital – spherical • p Orbital – dumbbell shaped • d Orbital – complex shapes (usually fourleaf clovers)Here you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termiEnjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube


Orbital Shape Orientationt


Chemistry Chp 5 Electrons In Atoms Powerpoint
Larger elements have additional orbitals, making up the third electron shell Subshells d and f have more complex shapes and contain five and seven orbitals, respectively Principal shell 3n has s, p, and d subshells and can hold 18 electrons Principal shell 4n has s, p, d, and f orbitals and can hold 32 electronsS Orbital Versus P Orbital While orbital numbers (eg, n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time The smallest sphere is 1s• Orbital – a 3D region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons • s orbital – spherical • p Orbital – dumbbell shaped • d Orbital – complex shapes (usually fourleaf clovers)



C Electron Config Prezentaciya Onlajn



Quantum Numbers Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt Qxkteh
Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a clover shape The last d orbital resembles a p orbital with a donut wrapped around the middle 4s 3s 2s 1s 2p 3p 3d ENERGY n l ml ms 1 0(s) 2 0(s) 1(p) 0 0 1, 1 0, 3 0(s) 1(p) 0 1, 1 0, 2(d) 1, 1, 0, 2, 2 4 0(s) 0 Movie periodic table of the elements t10 22/09/99 * 22/09/99 * 22/09/99Atomic Orbitals A Electron Location • Sublevel –Shape of electron cloud • s = spherical • p = dumbbell • d = too complex • f = too complex • 1st E level has 1 sublevel s • 2nd E level has 2 sublevels s and p • 3rd E level has 3 sublevels s, p, and d • 4th E level has 4 sublevels s, p, d and fSs sp sd pp pd dd HH LiH HC HN HF HPd in palladium hydride CC PP SS FS in SF6 FeFe However, the atomic orbitals for bonding may not be "pure" atomic orbitals directly from the solution of the Schrodinger Equation Often, the bonding atomic orbitals have a character of several possible types of orbitals


Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Atomic And Molecular Orbitals
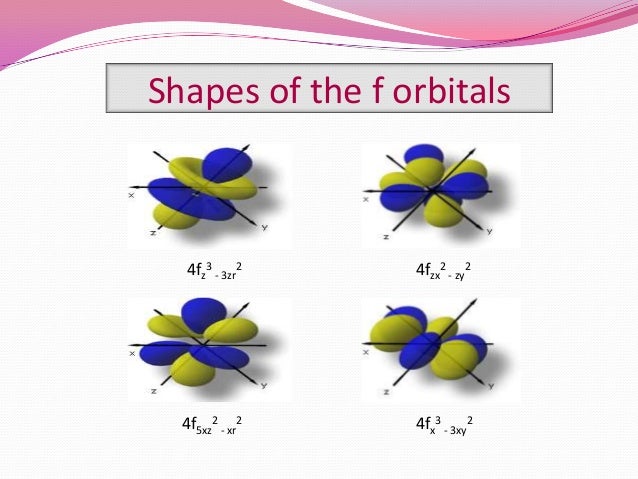
An illustration of the shape of the 1s, 2s and 3s orbitals The s sub shell can hold a maximum of two electrons as there is only one orbital S orbitals are spherical in shape and increase in size as the energy level or shell increasesA sorbital has a spherical shape A porbital has a 3dimensional dumbbell shape There are three porbitals, p x, p y, and p z at right angles to one another The structures of d and forbitals are more complexThe porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;


Orbital Shape Orientationt



Orbits And Orbitals Klm Vs Spdf Klm And Spdf Klm Old Style Lettering For The Shells Or Orbits K Is Closest To The Nucleus L Is Next M N O P Ppt
DOrbital Shape The d orbital is a clover shape because the electron is pushed out four times during the rotation when an opposite spin proton aligns gluons with three spinaligned protons Dumbbell shape of d orbital due to four points in rotation where sum of forces is not at 3d distance DOrbital Proton Fill OrderSHAPES OF ATOMIC ORBITALS S, P, D and FThe shapes of p, d and forbitals are described verbally here and shown graphically in the Orbitals table below The three porbitals for n = 2 have the form of two ellipsoids with a point of tangency at the nucleus (the twolobed shape is sometimes referred to as a " dumbbell "—there are two lobes pointing in opposite directions from each other)



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Determination Spd Videos Examples



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families
For example, the electron orbitals with aA PowerPoint presentation that begins with some review of electron configurations and noble gas electron configurations before transitioning into the shapes of electron clouds and orbitals (s, p, d, f) as well as comparing and contrasting the orbitals It also includes a youtube link to the Cassiopeia Project Wave FunctionFootnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshell



Orbitals
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
The subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum s 1 orbital, 2 electrons p 3 orbitals, 6 electrons d 5 orbitals, 10 electrons f 7 orbitals, 14 electrons Answer linkThe shapes of p, d and forbitals are described verbally here and shown graphically in the Orbitals table below The three porbitals for n = 2 have the form of two ellipsoids with a point of tangency at the nucleus (the twolobed shape is sometimes referred to as a "dumbbell"—there are two lobes pointing in opposite directions from each other)The magnetic (third) quantum number 'm l ' Has integral values between 'l' and 'l', including 0;



Ppt Quantum Numbers And Orbital Energies Each Atom S Electron Has A Unique Set Of Quantum Numbers To Define It N L Powerpoint Presentation Id



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333
The value of sin 2 x has no negative values ;Presentation Summary Atomic Orbitals Shapes and Orientations of Orbitals 1s Orbital Sphere around the nucleus The one tells you that the electron is in the orbital closest to the The Second Orbital Is "p" It Has A Dumbbell Like Shape There PPT Presentation Summary The second orbital is "p" It has a dumbbelllike shapeORBITAL HYBRIDIZATION The question of shape!



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Quantum Wave Model Electron Configuration 4 Subshells S P D F Ppt Download
Summary p orbitals and d orbitals p orbitals look like a dumbell with 3 orientations p x , p y , p z ("p sub z") Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a clover shape The last d orbital resembles a p orbital with a donut wrapped around the middle 9Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties homework assignment help is most useful online help portal for the students that providing all Online spdf Block Elements assignment help ServicesIn the long form of the periodic table, elements are grouped into four main blocks, purely on the basis of electronic configurationsElements are grouped in blocks 's', 'p', 'd' and 'fWe need next to examine the relationship between isolated atoms (with valence e s in s,p, and d orbitals – A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as a Flash slide show) on PowerShowcom id 74b2e0ZDI1M



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



High School Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
There are four different kinds of orbitals, denoted s, p, d and f each with a different shape Of the four, s and p orbitals are considered because these orbitals are the most common in organic and biological chemistry An sorbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a porbitals is dumbbellshaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shapedOrbital Diagram • Orbital diagrams are a visual way to represent the electron configuration by showing each of the orbitals and the spins on the electrons • This is done by determining the subshell (s,p,d,f) then drawing in each electron according to the rules 1 The Aufbau Principle 2 Pauli Exclusion Principle 3 Hund's Rule



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Q Tbn And9gcqtt Cp 5mdtmvkjxdr8vsbl1f8ma7ho6bkfldai4nhktcp2q Usqp Cau



Quantum Wave Model Electron Configuration 4 Subshells S P D F Ppt Download



Objectives To Learn About The Shapes Of The S P And D Orbitals Ppt Video Online Download



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



Quantum Numbers



Quantum Numbers The Easy Way Youtube


Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Electron Configuration Revised By Ferguson Spring Ppt Download



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals S P D And F Youtube



Orbital Diagrams Ppt Download
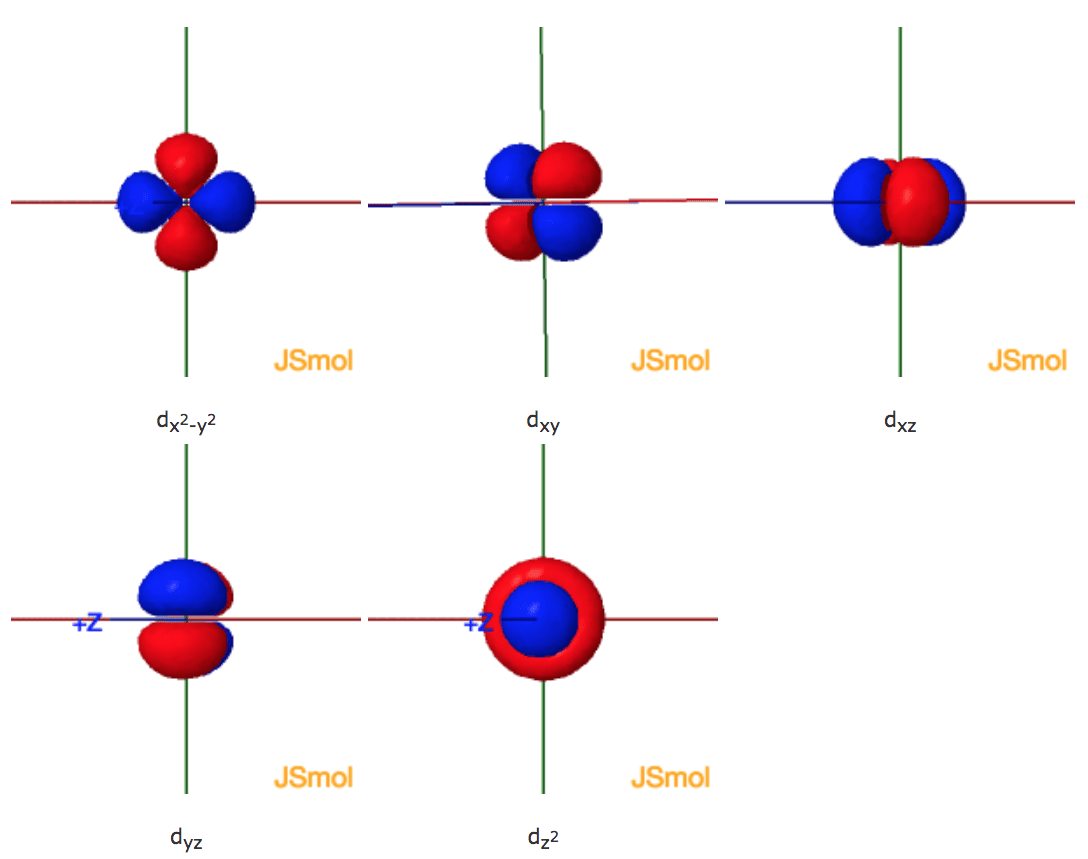


Shapes Of The 3d Orbitals In 3d



1 2 3 Orbitals And The Periodic Table Orbitals Grouped In S P D And F Orbitals Sharp Principle Diffuse And Fundamental Fine Orbitals Grouped Ppt Download



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Part 1 S Orbital Chemistry For Class 11 In Hindi Youtube



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital


Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Part 5 Shapes Of The Atomic Orbital S P D And F Orbital Atomic Structure Youtube



High School Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic


Orbital Shape Orientationt
/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



C Electron Config Online Presentation



Orbital Diagrams Ppt Download


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels



High School Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
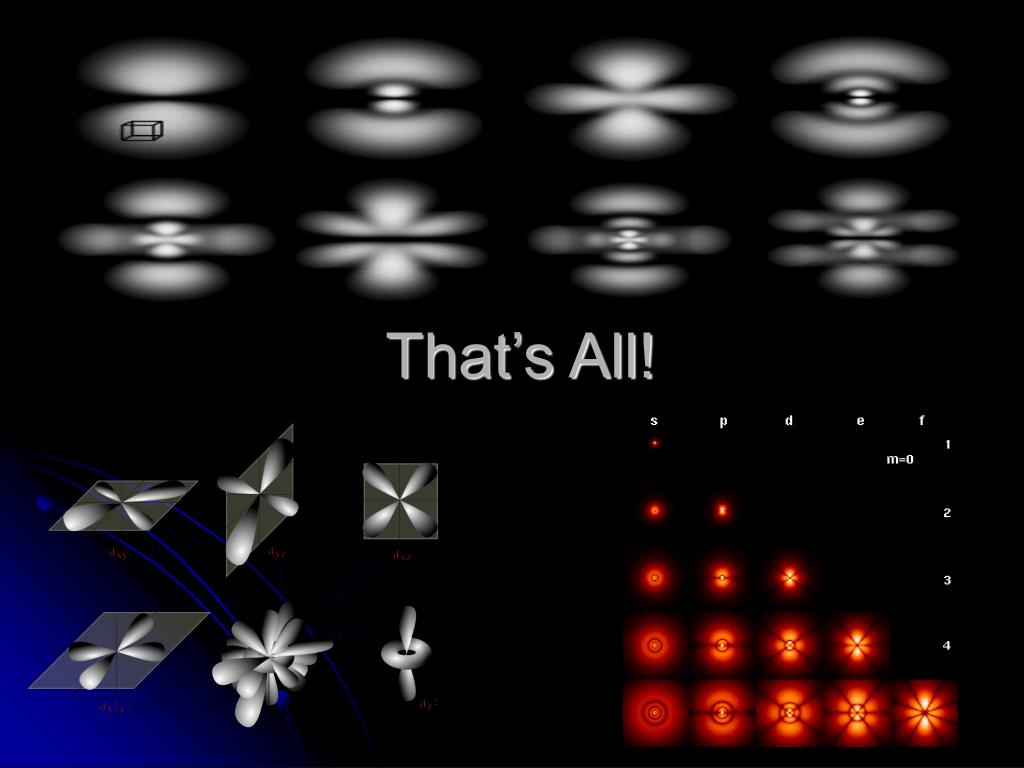


Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Draw The Shapes Of S P And D Orbitals Brainly In
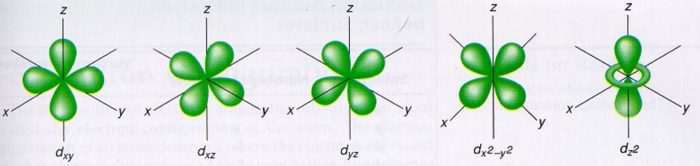


Shapes Of Atomic Orbital Chemistry Class 11 Structure Of Atom



S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
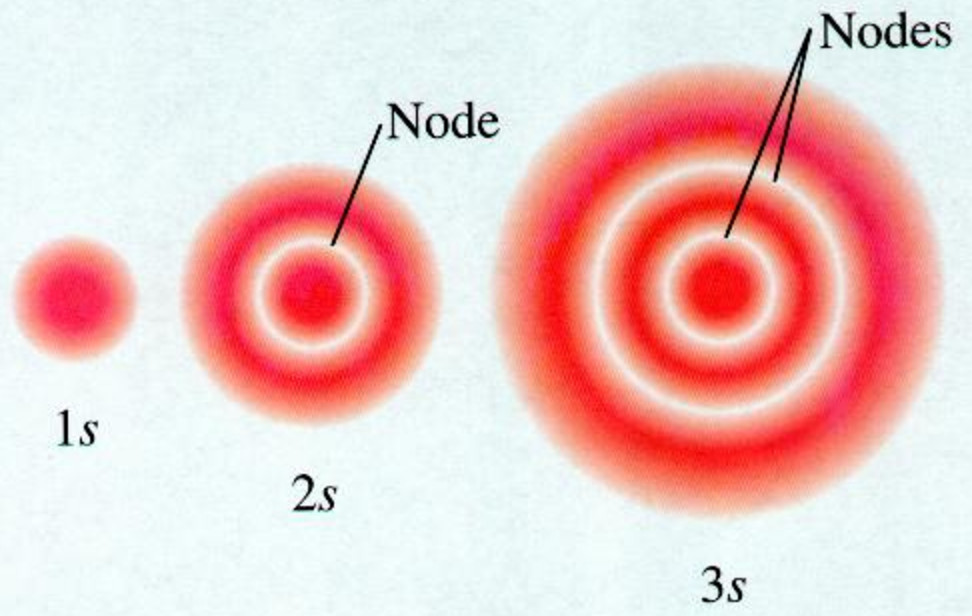


Shapes Of Atomic Orbital Chemistry Class 11 Structure Of Atom


Iu South Bend Chemistry And Biochemistry Ppt



Atomic Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt Yzf4hg


Q Tbn And9gcs9cc8nthz7ecpdnrlucjiamboqq Hkvswgwix0owhtjy2 Ktmv Usqp Cau



Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



1 2 3 Orbitals And The Periodic Table Orbitals Grouped In S P D And F Orbitals Sharp Principle Diffuse And Fundamental Fine Orbitals Grouped Ppt Download
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/antibonding-5b54ef9046e0fb005b6d11a9.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Draw The Shape Of S And P Orbitals Brainly In


How Do You Draw S P D F Orbitals Socratic



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333



Chapter 7 Atomic Structure And Periodicity Ppt Download


Sublevel Shapes Drone Fest



Ppt Atomic Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Electron Configuration H Cp Chemistry Chapter Ppt Download



Ib Chemistry Topic 12 1 Electronic Configuration



S P D F Obitals Notation Shapes Diagrams How To Work Out Electron Arrangements Configurations Order Of Filling Quantum Levels Electronic Structure Of Atoms Gce A Level Revision Notes



Quantum Mechanics Ppt Download



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Determination Spd Videos Examples
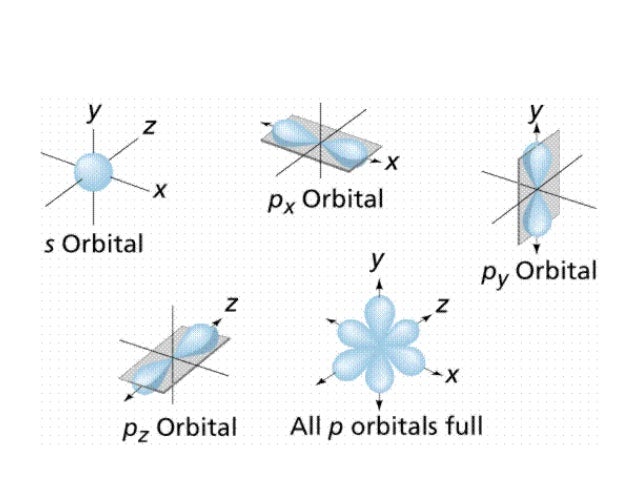


Orbital Shape Orientationt



Shape Of Orbitals
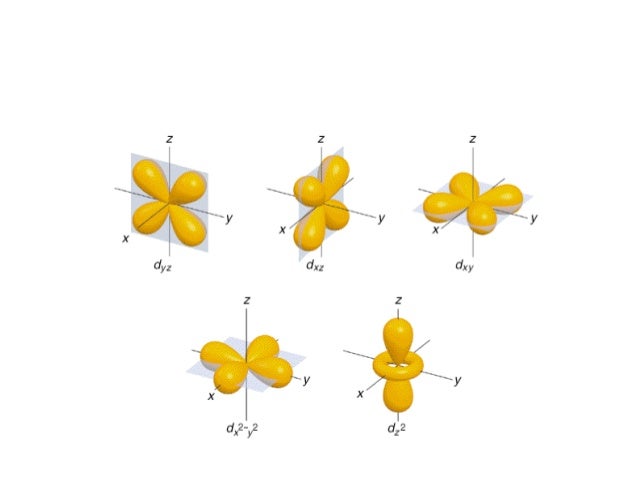


Orbital Shape Orientationt
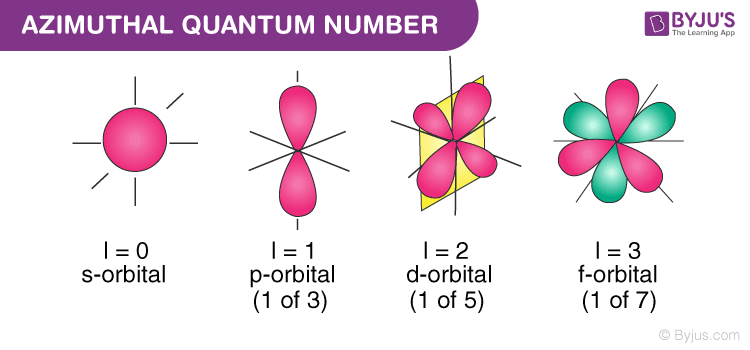


Azimuthal Quantum Number Definition Magnetic Quantum Number



12 1 5 Draw The Shape Of An S Orbital And The Shapes Of The P X P Y And P Z Orbitals Youtube
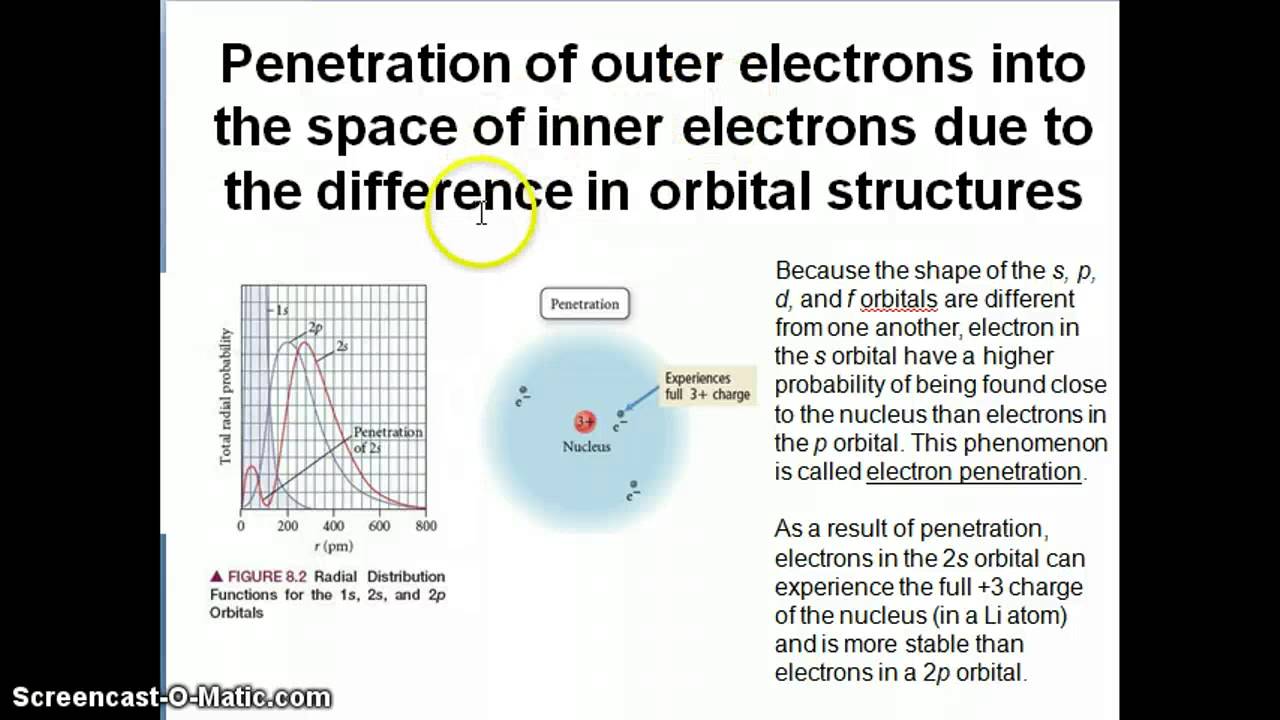


Orbital Shielding And Penetration Youtube



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Atomic And Molecular Orbitals



Electron Configuration Ppt Video Online Download
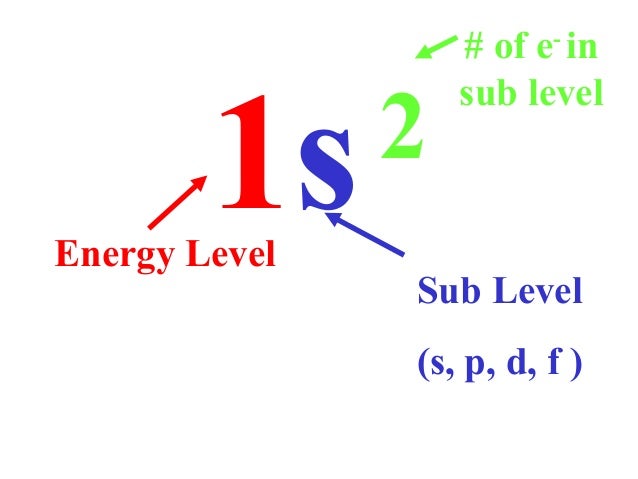


Orbital Shape Orientationt



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Worksheet Printable Worksheets And Activities For Teachers Parents Tutors And Homeschool Families



Chapter 5 Electrons In The Atom What Is An Atom Ppt Download


コメント
コメントを投稿